MADFLUX
Cooling Cities with Flow — One Patch at a Time
Introduction
Cities occupy only a small fraction of the Earth's surface, yet they consume a disproportionate share of energy and resources. As urban areas expand, concrete-heavy development, reduced vegetation, and disrupted airflow turn cities into heat traps—impacting health, equity, and environmental sustainability.
MADFLUX is a student-led community initiative at PSBB KKN, Chennai, created to address these challenges through science, innovation, and collective action.
The Problem: Urban Heat Islands
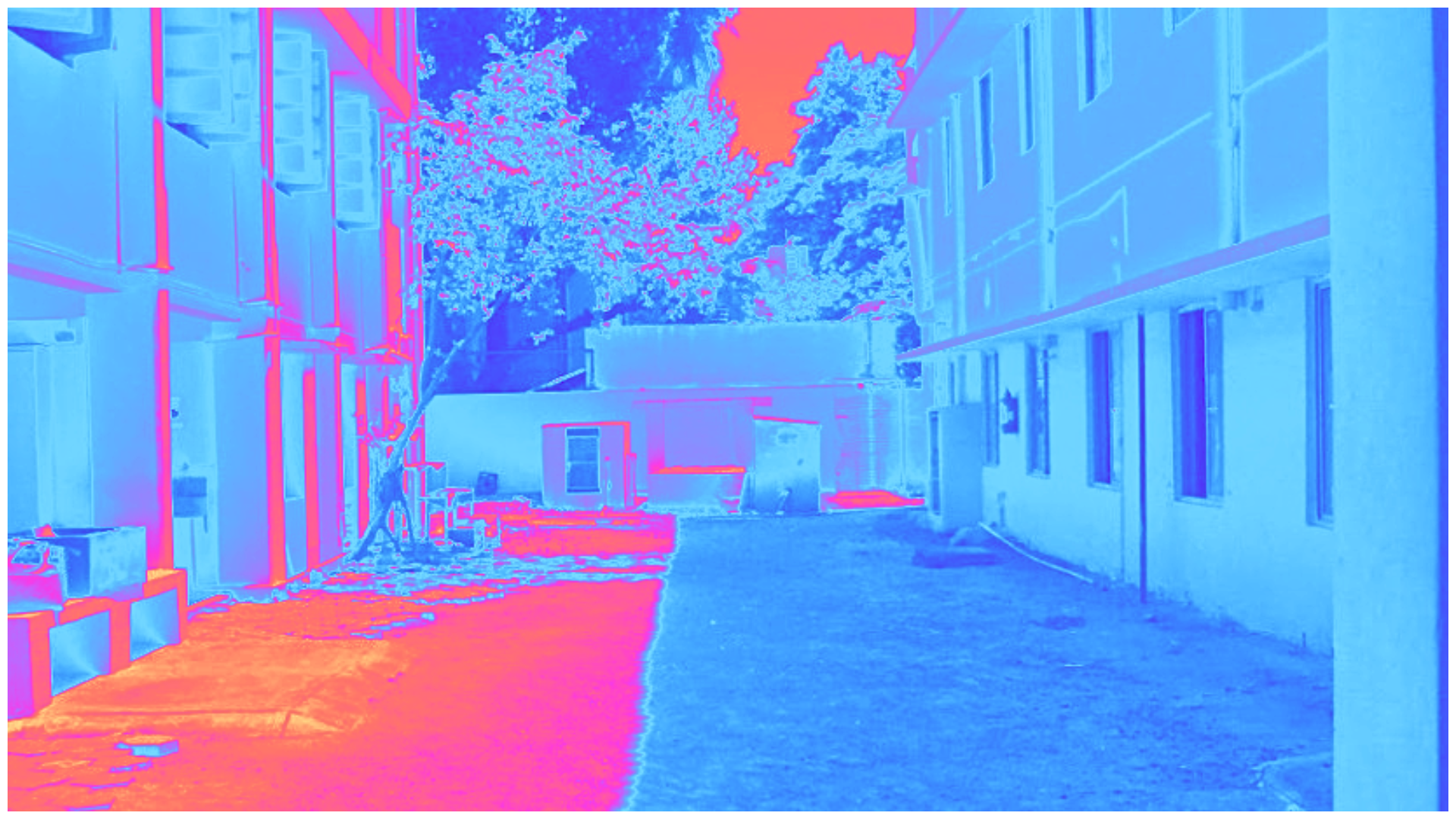

Urban Heat Islands: How cities absorb and trap heat
Urban Heat Islands (UHIs) occur when natural land surfaces are replaced by buildings, roads, and pavements that absorb and retain heat. This leads to:
• Higher local temperatures
• Increased energy demand for cooling
• Poor air quality
• Reduced outdoor comfort and wellbeing
UHIs disproportionately affect vulnerable communities and intensify the impacts of climate change in cities.
Our Approach: From Analysis to Action
MADFLUX bridges the gap between theory and real-world impact by combining:
• Digital Twin modeling
• CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) simulations
• Live environmental sensing
• On-ground implementation
We call this integrated model the Virtual Physical Thermal Environment Replica (VPTER).
Urban Refresh Zones (URZs)
Using VPTER, we identified heat-stressed areas on our school campus and redesigned them as Urban Refresh Zones—spaces that actively reduce heat and improve comfort.
Each URZ is planned virtually before being built physically, ensuring efficiency, scalability, and measurable impact.
On-Ground Transformation
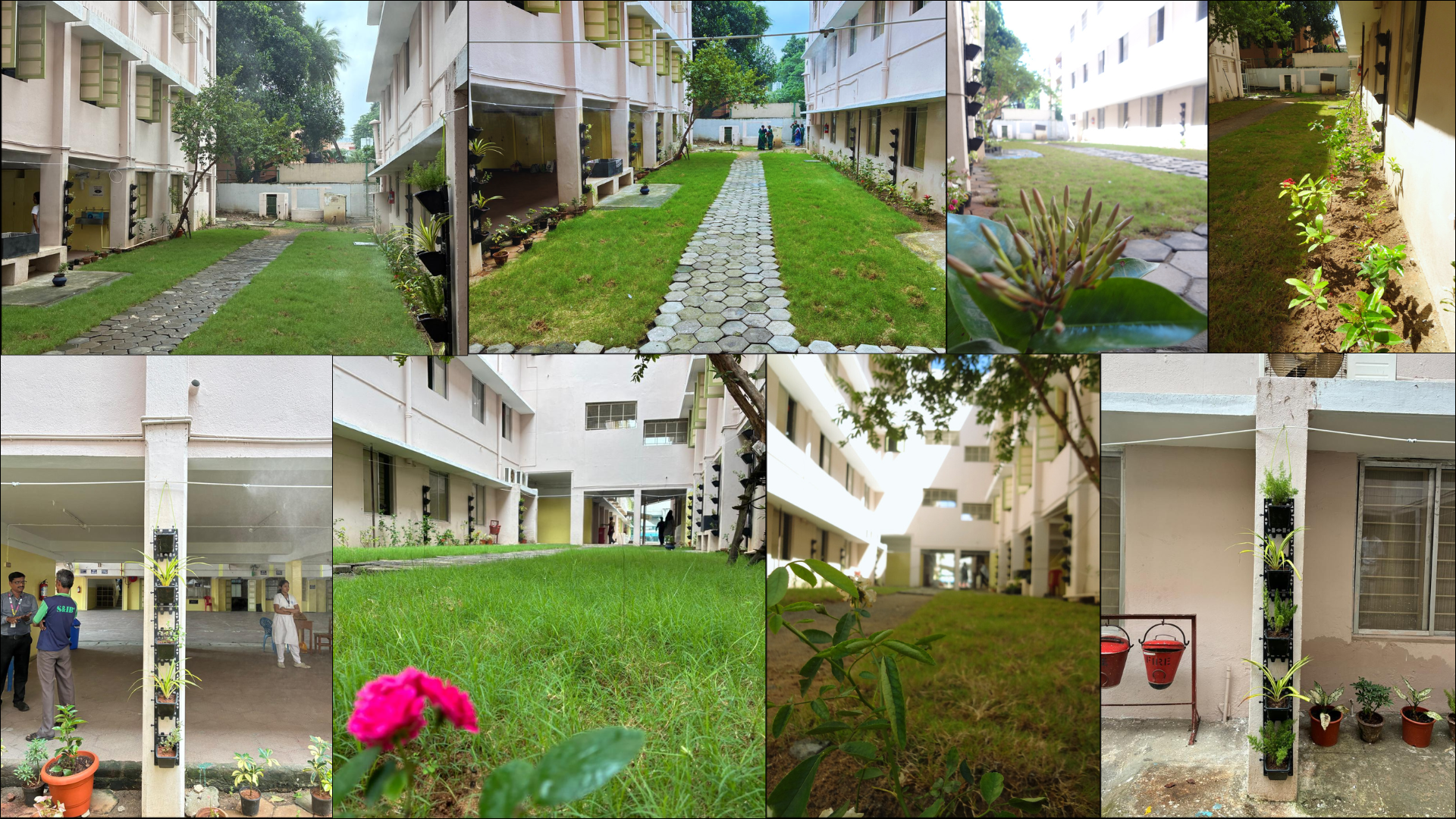

On-Ground Transformation: Real-world implementation of cooling zones
What was once a barren, heat-absorbing space has been transformed into a cooler, breathable environment featuring:
• Vertical gardens and native vegetation
• Bermuda grass and permeable surfaces
• Fogger-based evaporative cooling
• Optimized wind-flow corridors
This transformation demonstrates how thoughtful design can reshape microclimates.
Inside the Digital Twin (VPTER)
The VPTER integrates multiple layers of analysis:
• Wind speed and direction modeling
• Surface and ambient temperature mapping
• Placement optimization for foggers and greenery
• Water efficiency and airflow simulations
This allows us to test, refine, and scale solutions before physical deployment.
EvapFog Tiles: Passive Cooling Innovation
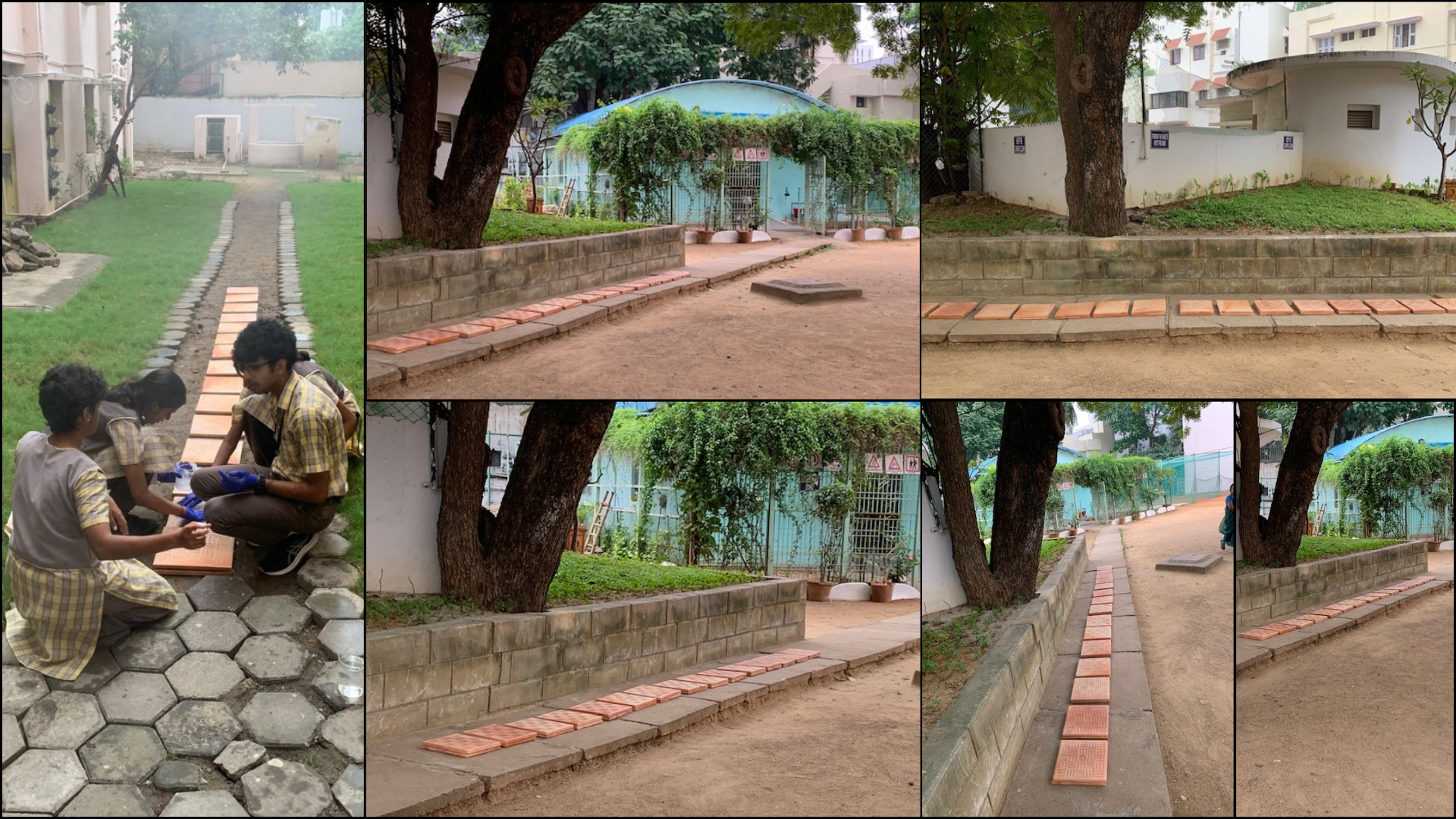

EvapFog Tiles: Innovative passive cooling technology
EvapFog Tiles are a low-cost, passive cooling solution designed for hot climates.
How they work:
• Double-layered porous terracotta structure
• Sodium polyacrylate retains moisture
• Heat triggers evaporation, reducing surface temperature
Results:
• Significant cooling compared to concrete
• No electricity required
• Locally manufacturable and scalable
Implementation & Cost Efficiency
MADFLUX follows a phase-wise implementation model:
• PSBB KKN Pilot (Completed): ₹96,525
• Campus Expansion Phase: ₹1,80,000
• Locality-Scale Deployment: ₹18–27 lakh
This makes the model affordable, replicable, and suitable for schools, campuses, and neighborhoods.
Challenges & Learnings
Key challenges and solutions included:
• Plant stress: Use of heat-resilient native species and fogger automation
• Monsoon flooding: Elevated systems and drainage simulations
• Funding: Community-driven, low-budget execution
• Maintenance: Student-led monitoring and weekly assessments
• Water usage: Integration with rainwater harvesting
Each challenge strengthened the system design.
Community Impact & Feedback
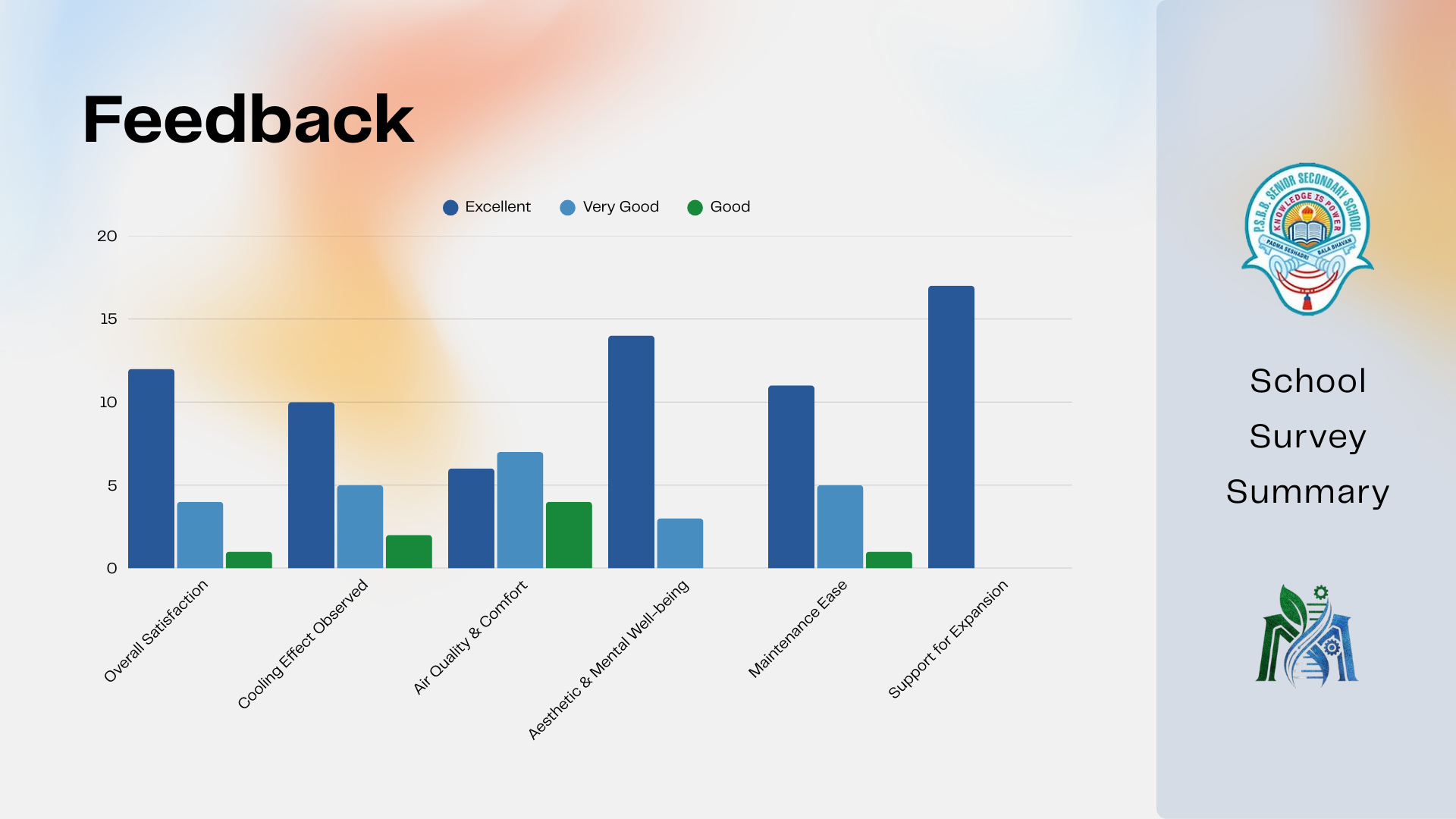
Community Impact & Feedback: Positive response and participation
Community surveys revealed:
• Average perceived temperature reduction of 3.5°C
• 65% preference for green pathways
• 82% willingness to participate and volunteer
Beyond cooling, the project enhanced mental wellbeing, aesthetics, and community ownership.
Beyond Cooling: Expanding Innovation

Beyond Cooling: Expanding Innovation to related sustainability solutions
Symbiotic Air Catharsis Module A conceptual system that captures indoor CO₂, converts it into usable energy, and supports air purification—creating a partially self-sustaining loop.
Flood Mitigation Concepts Mathematical drainage and underground storage models designed to reduce urban flooding, developed as part of student research initiatives.
Scaling from Campus to Community
MADFLUX is designed to scale:
• From micro-spaces to neighborhoods
• From campuses to entire localities
• Through open tools like QGIS and OpenFOAM
Knowledge, designs, and learnings are shared openly to encourage replication.
Community Engagement & Outreach
MADFLUX is more than infrastructure—it is a movement.
• Student-led awareness programs
• Environmental drives and clean-up initiatives
• A growing digital presence and blog
• Continuous dialogue with the local community
The project thrives on participation and shared responsibility.
Our Vision
Sustainable cities are not built by technology alone. They are built by informed, engaged communities working together with purpose.
MADFLUX proves that when youth lead with science, empathy, and action, even small interventions can create lasting change.
Cool your city with flow — one patch at a time.